Accounting software for self-employed
professionals in Switzerland
Compare Swiss accounting software for freelancers and sole proprietors. Learn what you must track (QR invoices, expenses, VAT/MwSt/TVA), which features matter, and see pricing-focused options—plus FAQs and a simple tool chooser.
If you’re self-employed in Switzerland, accounting software isn’t just about “doing books”—it’s about getting paid faster, staying VAT-compliant (MwSt/TVA), and making tax time painless (for you and your fiduciary / Treuhänder). This guide gives you a practical checklist of what you must track, what features to look for in Swiss accounting tools (including QR invoice / QR-Rechnung / facture QR support), and a comparison of popular options—ending with a clear recommendation based on how you work.
Last updated: January 31, 2026 (pricing and plan features can change—review quarterly).
Note: This is general information, not tax or legal advice. Requirements can vary by canton and your specific situation.
What “self-employed” means in Switzerland (and why it matters for accounting)
In Switzerland, “self-employed” typically means you operate as a sole proprietor (Einzelunternehmen / raison individuelle) or similar structure where you personally run the business and are responsible for its administration.
That affects accounting in three big ways:
- You’re responsible for accurate records of income and expenses (even if you hire a fiduciary later).
- You may need to manage VAT (MwSt/TVA) depending on turnover and activity.
- You need clean documentation (invoices, receipts, bank proof) to support your tax declaration and business results.
Many freelancers start with spreadsheets—until they hit the first “Swiss reality checks”: QR invoices, mixed private/business bank transactions, clients paying late, VAT questions, and year-end reporting. Good software reduces all of that friction.
The Swiss self-employed compliance checklist: what you must track
Think of your accounting setup as repeatable weekly workflows. The goal isn’t perfection—it’s traceability (you can explain each number) and audit-ready documentation (you can prove it).
- 🧾Invoices (incl. Swiss QR invoices)
Professional invoices that are easy to pay—and easy to reconcile.
- 📸Expenses + receipt retention
{ "Proof-first bookkeeping": "each expense should have a receipt and a category." }
- 🧮VAT (MwSt/TVA)
VAT-ready invoices, correct rates, and clean reporting by period.
- 🏦Cash flow + buffers
Ongoing visibility so taxes and AHV/AVS don’t become surprises.
- Invoice #3
Magic Heidi
CHF 500
Jan 29
- Invoice #2
Webbiger LTD
CHF 2000
Jan 24
- Invoice #1
John Doe
CHF 600
Jan 20
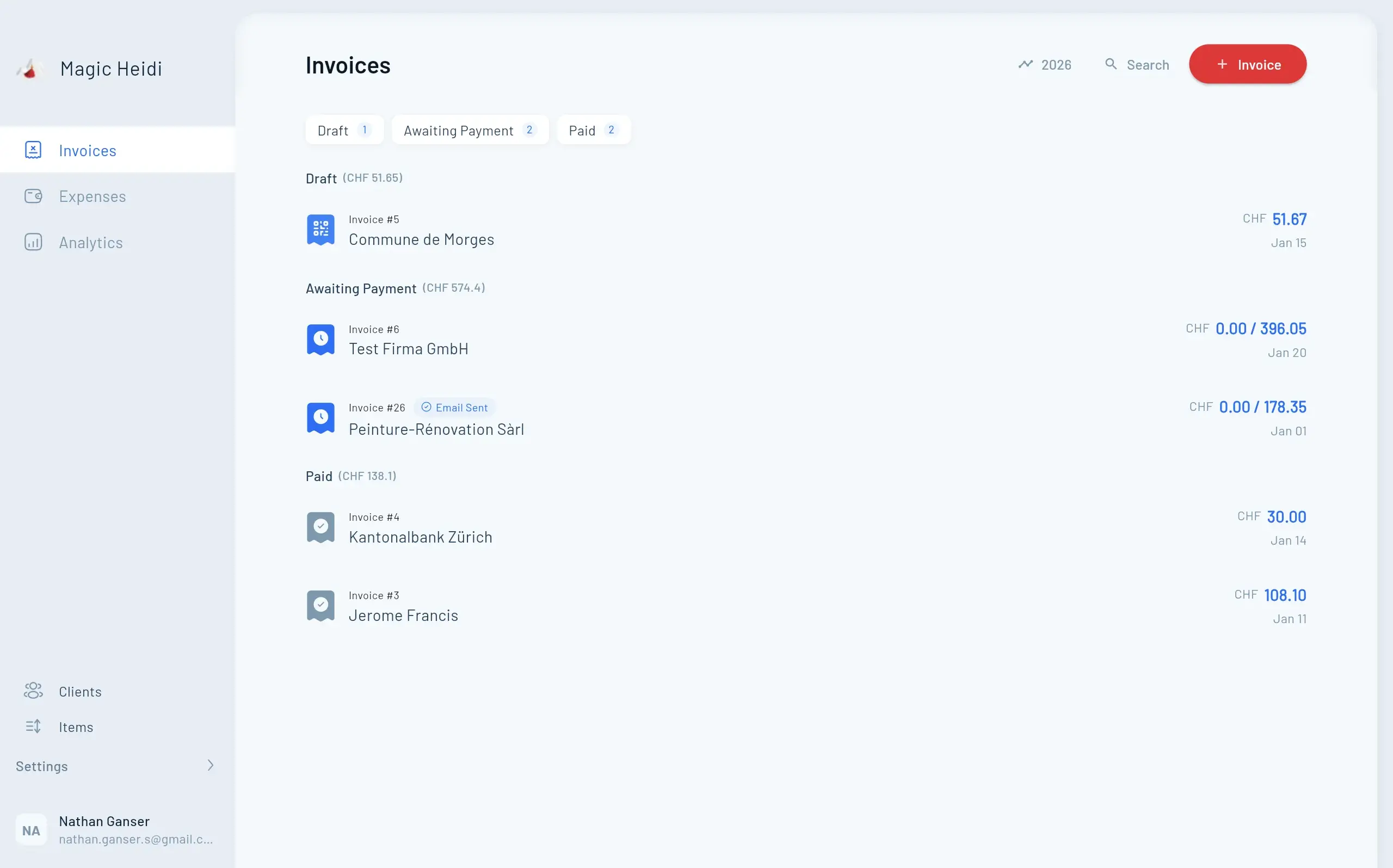
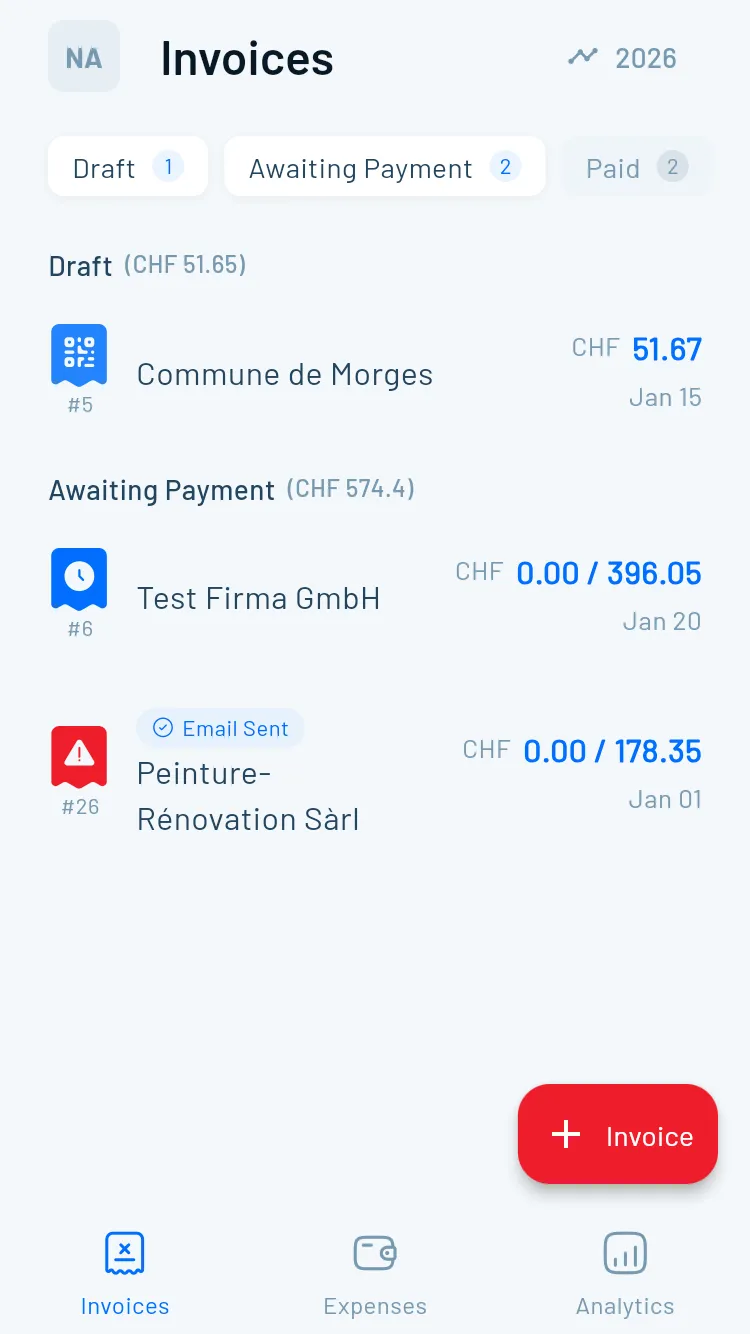
Invoices that get you paid faster with QR billing
At minimum, you need invoices that are clear, professional, and easy to pay. In Switzerland, customers increasingly expect QR invoices (QR-Rechnung / facture QR) “out of the box”. Cleaner invoices = faster payment, fewer back-and-forth emails, and easier bank reconciliation.
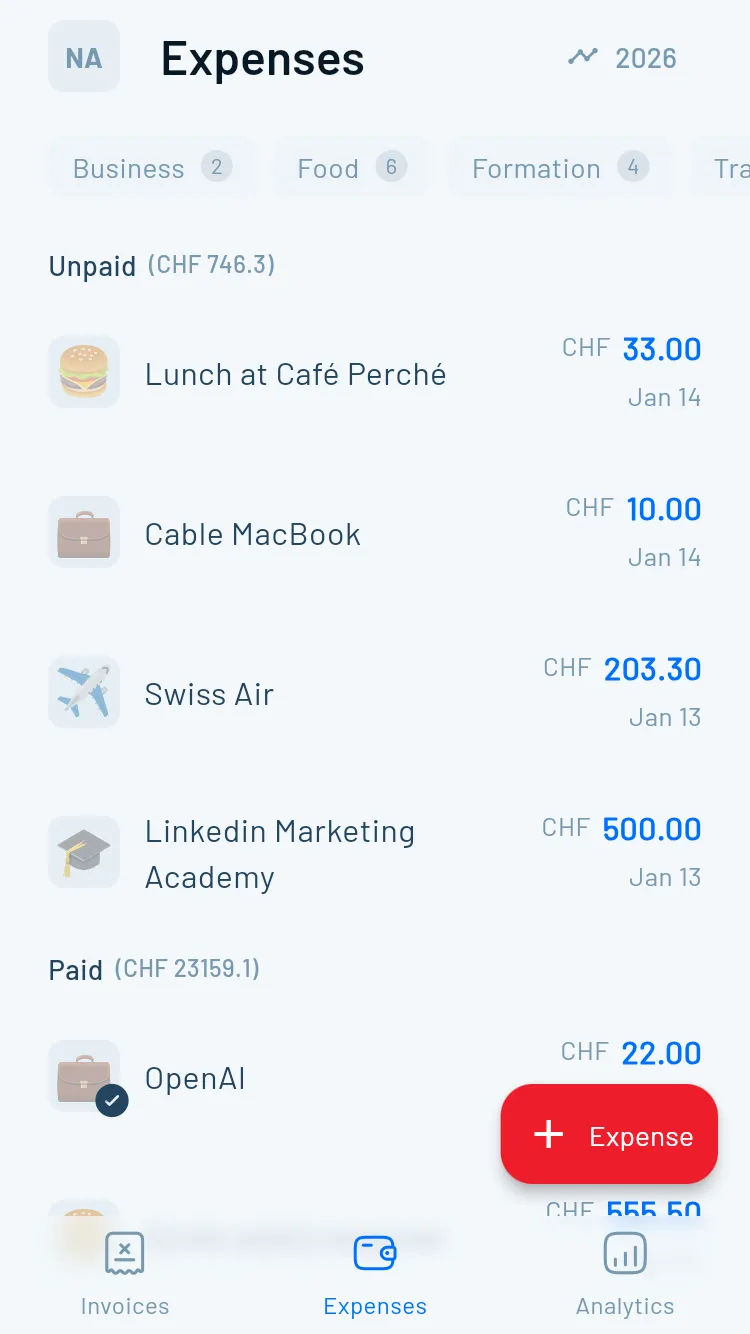
Expenses you can actually prove
Swiss bookkeeping isn’t only about totals. It’s also about proof. Track amount, date, supplier, category, VAT treatment (if VAT-registered), and keep the receipt (photo/PDF) attached to the transaction—so you’re not hunting through email and camera rolls at year-end.
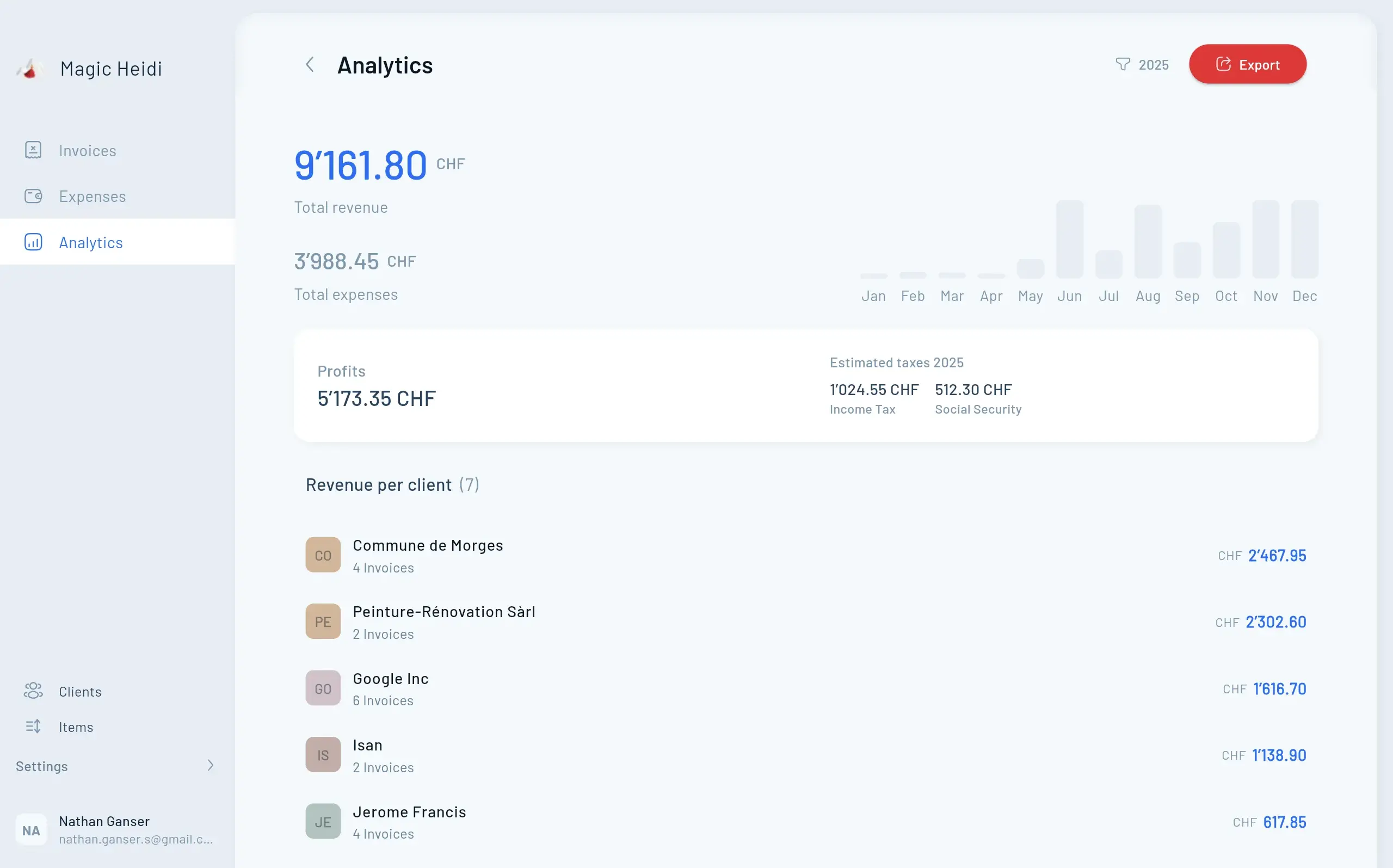
VAT (MwSt/TVA): threshold, workflow, and “voluntary VAT”
VAT is one of the main reasons self-employed people in Switzerland upgrade from spreadsheets. Even if your business is simple, VAT adds structure:
- You may need to register for VAT once you pass the turnover threshold (and in some cases, you can register voluntarily).
- You must issue invoices with the correct VAT handling and keep VAT evidence.
- You’ll typically need periodic VAT reporting and clean totals by rate.
What software should do here: Swiss VAT rates and reporting logic built-in, the ability to mark transactions correctly, and exports you can share with a fiduciary.
Tip: If you’re unsure whether you should register or how to treat VAT in edge cases, ask a fiduciary. The right software makes it easier to provide clean data—but it can’t replace professional advice.
Cash flow + AHV/AVS planning (avoid surprises)
Even without payroll, self-employed people should treat cash flow as a compliance-adjacent task: you want to consistently set money aside for taxes and social security (AHV/AVS), based on your actual results.
A simple approach many freelancers use:
- Track income and expenses weekly
- Maintain a “tax + AHV buffer” sub-account or separate bank account
- Review monthly: revenue, margin, upcoming payments
What software should do here: real-time profit visibility, bank feeds/imports, and categories that make your year-end numbers believable.
What to look for in Swiss accounting software
(quick shortlist)
Not all “accounting software” is Switzerland-ready. Use this checklist to shortlist tools quickly.
Swiss QR invoice / QR-bill support
Non-negotiable for many Swiss clients. Verify QR invoice generation, correct payment details, and clean PDFs.
- QR invoice generation aligned with Swiss expectations
- Correct handling of QR-IBAN vs IBAN (where relevant)
- Clean PDF output + multilingual templates (DE/FR/IT/EN)
VAT (MwSt/TVA) that matches your reality
If you’re VAT-registered (or may become VAT-registered), you want VAT features that prevent mistakes and simplify reporting.
- Swiss VAT rates and correct calculation
- VAT-ready invoicing
- VAT summaries and exports by period
- VAT-exempt invoices when applicable
Bank import + reconciliation
For most self-employed people, the biggest automation win is reducing manual entry and matching payments correctly.
- Bank statement import (CSV/CAMT where available)
- Match invoice payments to bank transactions
- Simple rules for recurring transactions
- Clear “paid/unpaid” status without spreadsheets
Receipt capture + documentation workflow
Your deductions are only as good as your proof. Attach receipts where you record the expense.
- Mobile receipt scanning
- Attachments per transaction
- OCR (optional, but a big productivity boost)
- Audit trail if you collaborate with others
Exports + fiduciary collaboration (Treuhänder-friendly)
Even if you do the work yourself, year-end often includes a fiduciary. Make handoff painless.
- Exports for invoices, expenses, journal/ledger as needed
- Easy sharing of documents (attachments included)
- Optional accountant access without extra complexity
- Clean data structure for year-end closing
Pricing that fits self-employed economics
Pricing isn’t only the cheapest monthly fee—watch where key features are paywalled.
- Free tier that is actually usable
- Bank reconciliation / OCR / exports not locked too early
- Annual vs monthly discounts
- Predictable upgrades when your workload grows
Accounting software for self-employed in Switzerland: pricing + best use
Prices are public examples and can change. Confirm on each provider’s pricing page before deciding.
| Software | Best for | Swiss strengths | Typical pricing (public examples) | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magic Heidi | Self-employed who want an all-in-one toolbox (invoicing + expenses + accounting) without complexity | QR invoices, Swiss VAT rates, designed for Swiss self-employed workflows | If you need a full SME “ERP” stack, you may want a broader platform | |
| bexio | Growing businesses that want broader admin (accounting + more operations) | Strong ecosystem, positioned for SMEs | Can feel heavier than needed for solo freelancers | |
| KLARA | Modular “pick what you need” approach | Switzerland-focused, modular pricing | Modules/add-ons can make costs less predictable | |
| smallinvoice | Invoicing-first with a clear upgrade path | Strong invoicing focus; collaboration messaging for fiduciary | For deeper accounting automation, check plan scope carefully | |
| Banana Accounting | People who want desktop accounting and control | Offline/desktop style; familiar accounting structure | Less “mobile-first”; workflows can be more manual | |
| Swiss21 / AbaNinja ecosystem | Budget-sensitive users who want a Swiss ecosystem with a free start | Swiss-focused, popular entry point | Subscription changes from 01.01.2025; Pro referenced at CHF 49 from that date | Free tier limitations may push upgrades (automation/bank reconciliation/OCR/support) |
How to use this table:
- If you mainly invoice and track expenses, prioritize QR invoicing + receipt capture + simple exports.
- If you’re VAT-registered, prioritize VAT handling + reconciliation + clean VAT summaries.
- If you’re scaling, prioritize multi-user workflows + deeper reporting + integrations.
Quick chooser: which tool fits your situation?
Pick the profile that sounds most like you—then test-drive 2–3 tools with real invoices and real expenses.
Newly self-employed (simplest Swiss setup)
QR invoices, mobile receipts, simple profit view without jargon.VAT-focused (fewer mistakes)
Swiss VAT logic, summaries, and clean reconciliation.Price-sensitive (invoicing-first)
Usable free/low-cost plan with QR billing and basics.“I’m newly self-employed and want the simplest Swiss setup”
You want a tool that makes it easy to:
- Create QR invoices immediately
- Capture receipts from your phone
- See a simple profit picture without accounting jargon
Shortlist: Magic Heidi, smallinvoice (if you’re invoicing-first)
“I need VAT (MwSt/TVA) support and I want fewer mistakes”
You want:
- Swiss VAT logic built in
- Clear VAT summaries
- Bank import/reconciliation so payments and invoices match cleanly
Shortlist: Magic Heidi, KLARA, bexio (depending on complexity)
“I mostly need invoicing and I’m price-sensitive”
You want:
- A usable free tier or low-cost plan
- Professional invoice templates and QR billing
- Basic expense tracking
Shortlist: smallinvoice, Swiss21/AbaNinja ecosystem (review limitations), Magic Heidi (if you want accounting included)
“I prefer desktop software and I’m comfortable doing things manually”
You want:
- Offline control
- A classic accounting workflow
- Predictable annual pricing
Shortlist: Banana Accounting
“I’m scaling beyond solo: more processes, maybe employees later”
You want:
- Broader business admin features
- Multi-user access and structured workflows
- Reporting and integration options
Shortlist: bexio, KLARA (modular growth)
Why many Swiss freelancers choose Magic Heidi
Magic Heidi is positioned as an all-in-one toolbox for the Swiss self-employed—built for the day-to-day reality of invoicing, expensing, and basic accounting without making you feel like you’re running an enterprise finance department.
Magic Heidi tends to be a great fit if you:
- Want QR invoices and Swiss-friendly invoicing flows
- Prefer a straightforward system for expenses + receipts
- Want VAT-ready features without a steep learning curve
- Want a clean way to collaborate with a fiduciary later (exports, clear records)
- Don’t want to stitch together separate tools for invoicing and bookkeeping
Plans (as publicly shown):
- Free (limited to 3 invoices / 3 expenses)
- CHF 30/month
- CHF 299/year
FAQs: accounting software for self-employed in Switzerland
Do I need double-entry bookkeeping as a sole proprietor in Switzerland?
It depends on your size and situation. Many self-employed people can start with simpler income/expense tracking, but requirements can increase as revenue grows or based on legal form and reporting needs. If you’re unsure, ask a fiduciary—then choose software that can grow with you (or export cleanly if you upgrade later).
When do I need to register for VAT (MwSt/TVA) in Switzerland?
VAT registration depends on turnover and other factors, and some businesses register voluntarily. Confirm your specific threshold situation with official guidance or a fiduciary, then use software that supports Swiss VAT rates and reporting so you don’t rebuild your process later.
Can accounting software generate Swiss QR invoices correctly?
Many tools claim QR support, but you should verify it covers what you need (proper QR invoice PDF output and correct payment details). If clients in Switzerland expect QR invoices, treat this feature as a must-have.
Can I invoice in multiple languages (DE/FR/IT/EN)?
If you work across cantons—or with international clients—look for multilingual invoice templates and flexible wording fields. Even if your UI is English, your invoices may need to be German or French for client comfort.
Does it support importing bank statements and reconciling payments?
Bank import and reconciliation are among the biggest time-savers for freelancers. Look for support for bank statement imports (and any available bank feed options), and payment matching that connects invoice payments to bank transactions.
How do I share my data with a fiduciary / Treuhänder?
Choose software that offers exports of invoices and expenses, a ledger/journal export (if needed), and attachments included (receipts linked to transactions). Some tools also offer direct collaboration features or accountant access.
Is receipt scanning (OCR) necessary?
Not strictly, but it’s often worth it. OCR speeds up entry and reduces errors—especially with many small expenses (travel, meals, supplies). If you’re budget-sensitive, prioritize capture + attach first; add OCR when time savings justify the upgrade.
What records should I keep as a self-employed person?
Keep invoices you issued, supplier bills and receipts, bank statements and payment confirmations, and VAT documentation (if registered). Software helps when it stores receipts next to transactions and makes exports easy.
Can I switch tools later without losing everything?
You can, but switching is easier when your tool supports exporting invoices (PDF + data), client/contact lists, and expenses plus attachments. Before committing, check export options and whether attachments are downloadable in bulk.
What’s the best accounting software in Switzerland for freelancers?
The best choice depends on your workflow (invoicing-first vs full bookkeeping), VAT complexity, need for automation (bank reconciliation, OCR), and whether you collaborate with a fiduciary. Use the Quick chooser to shortlist 2–3, then test-drive them with real invoices and expenses.
A simple setup plan (so you actually stick with it)
If you want your accounting to stay “under control” year-round, set up a routine you can keep:
- Create invoices in the tool (use QR invoice format if you bill Swiss clients).
- Capture receipts immediately (mobile scan/photo → attach to expense).
- Import bank transactions weekly and reconcile payments.
- Monthly review (30 minutes): check unpaid invoices, top expense categories, and set aside money for taxes/AHV.
- Quarterly: export a report pack for your fiduciary (or for your own records).
Simple Pricing. No Surprises.
One plan. All features. Cancel anytime.
Free Trial
- 3 invoices
- 3 expenses
- All features unlocked
- No credit card required
Annual
- Unlimited invoices
- Unlimited expenses
- AI expense scanning
- All platforms included
- Bank statement import
- Swiss VAT management
- Priority support
Monthly
- Unlimited invoices
- Unlimited expenses
- AI expense scanning
- All platforms included
- Bank statement import
- Swiss VAT management
Try Magic Heidi: Swiss-ready invoicing, expenses, and accounting in one place
QR invoices, Swiss VAT support, expense tracking with receipts, and clean records for tax time—get started in minutes.