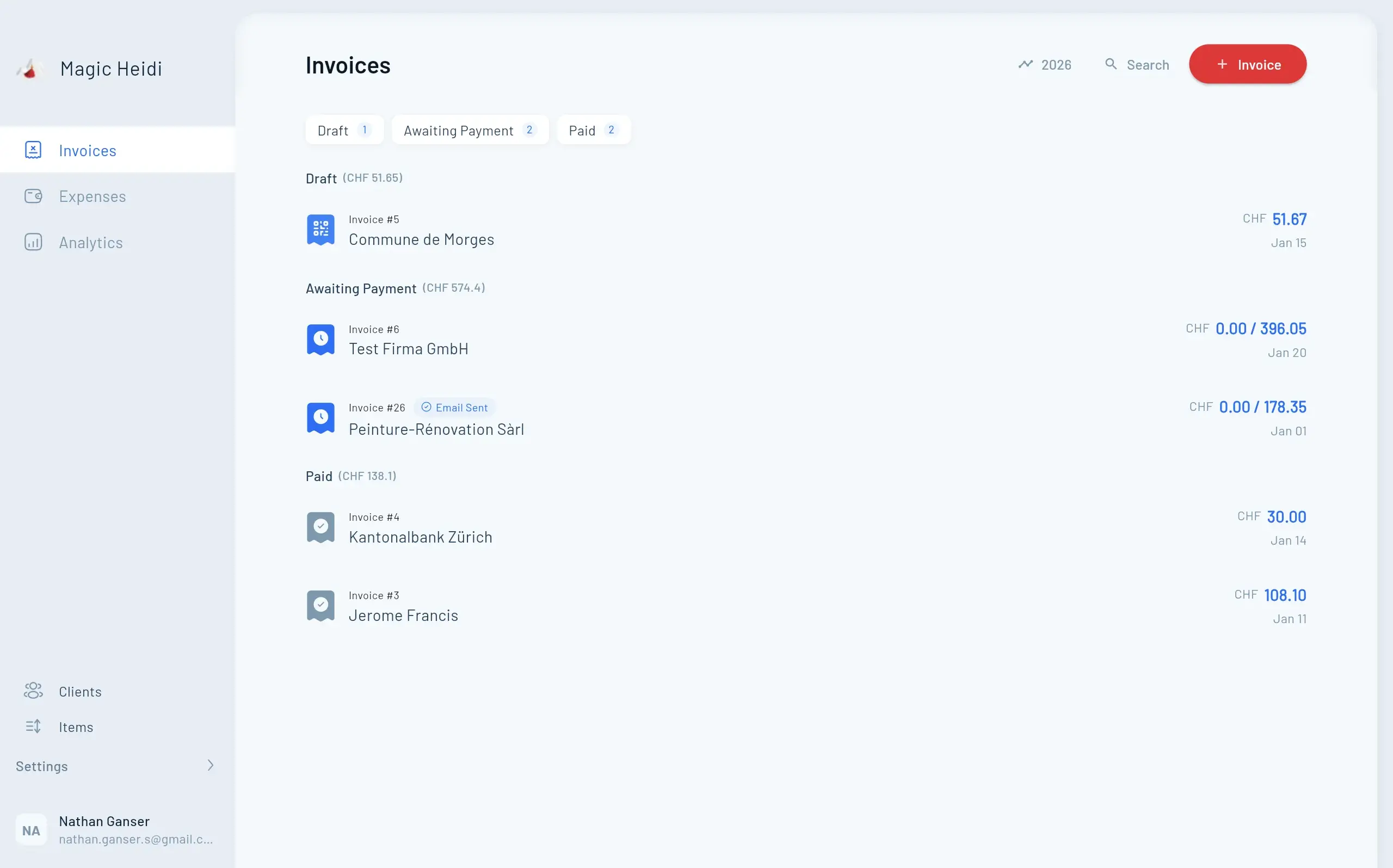
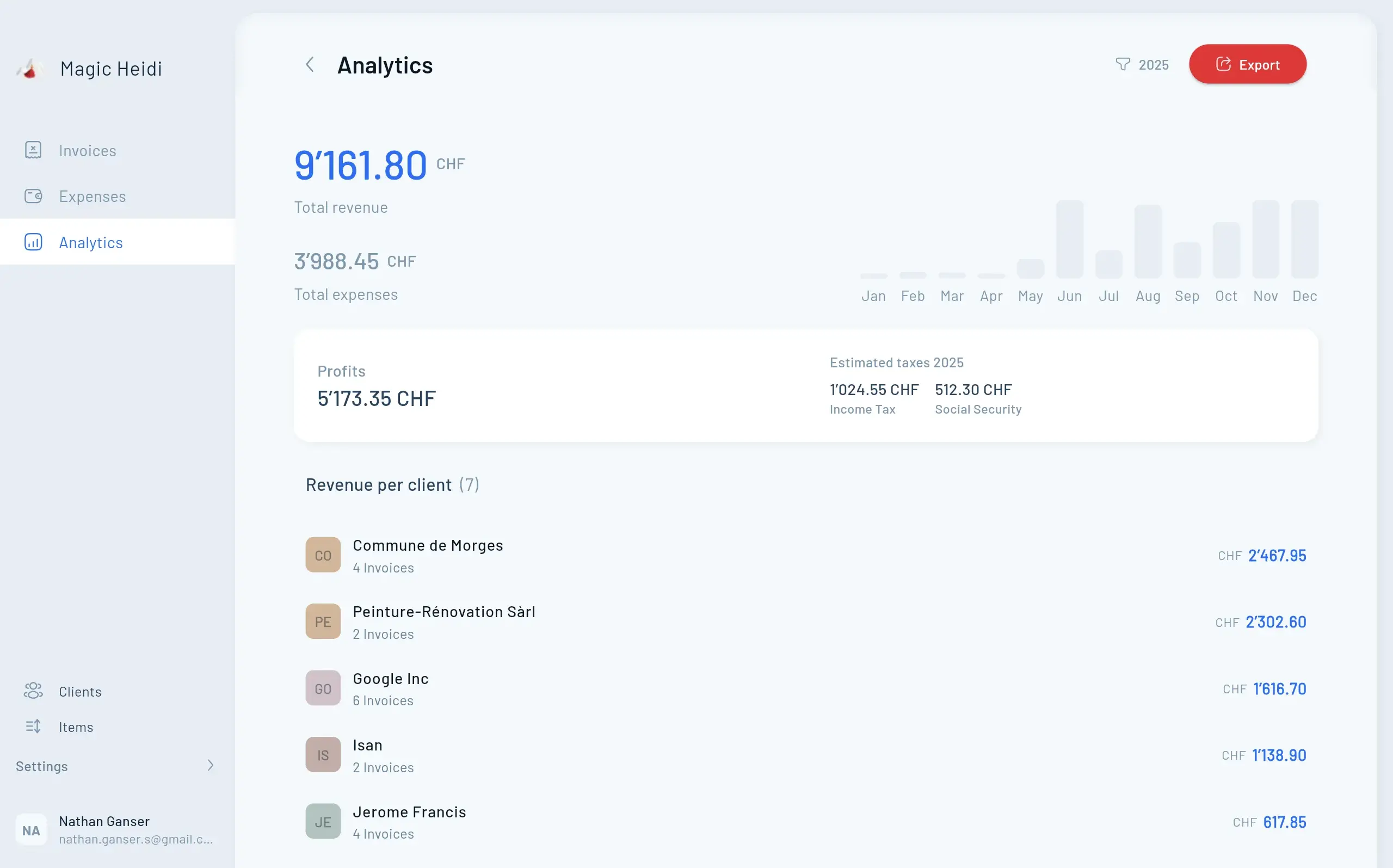
Request a QR-IBAN from Your Bank
Contact your Swiss bank to obtain a QR-IBAN. Most banks issue them automatically for business accounts.
- Existing Swiss business bank account required
- Confirm you'll be issuing QR-bills
- Usually no additional fees
- Tied to your existing account